Requires interaction between conforming surfaces.
Potentially Occurs in:
Bolted together machine components, gears, cams, slides, bushings, dry sliding systems, valves, sliding surfaces, bushings, hard-metal sliding systems
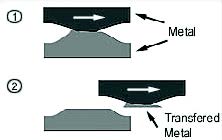
Adhesive wear is due to localized bonding between contacting solid surfaces leading to material transfer between the two surfaces or loss from either surface. The origin of this form of wear is in reality the same phenomenon that is responsible for friction. If two solids are in intimate contact, at least locally, there is a tendency for these solids to bond together.
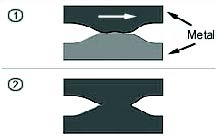
Seizure
Seizure is the stopping of relative motion as the result of interfacial friction. Local solid-state welding may be a part of the mechanism of seizure. This wear process does not necessarily require progressive loss of material.
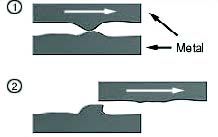
Galling
The term galling does not have an agreed on definition. In Europe, the wear community uses the term scuffing in its place. The Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development, Paris (OECD), defines scuffing as localized damage caused by the occurrence of solid-phase welding between sliding surfaces without local melting.
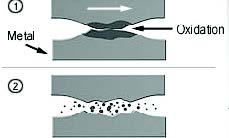
Oxidative Wear
Oxidative wear is a wear process in which sliding surfaces react with their environment to form oxide films that separate the surfaces. The wear exists in lightly loaded systems, and it is sometimes referred to as mild wear.